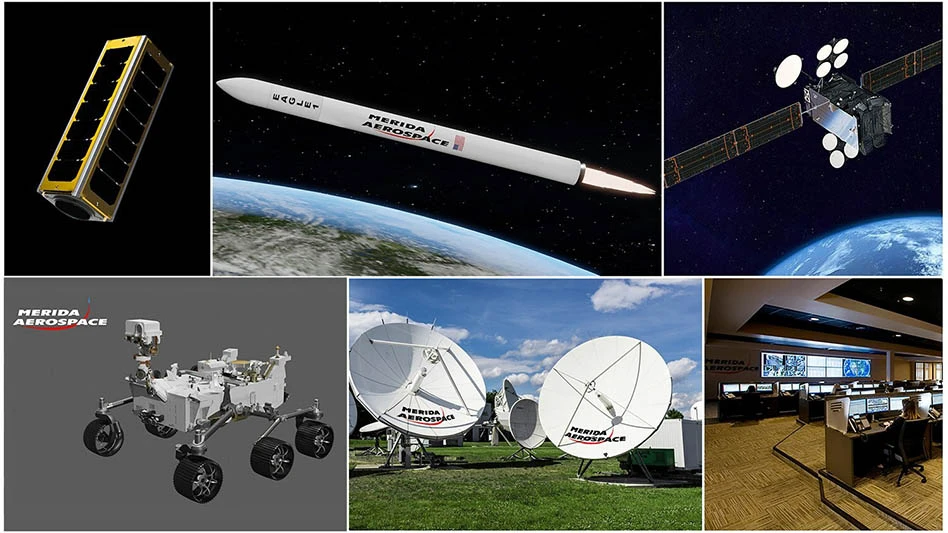
The space industry has undergone significant changes in recent years, and this transformation continues to evolve. Companies dedicated solely to rocket launches or satellite systems, CubeSats, and low-orbit satellites are increasingly falling behind. New space clients are seeking space companies offering comprehensive services, enabling them to fulfill their needs from start to finish and access all the necessary technology for their projects in one place with a single company.
Regrettably, such companies are still largely absent in the space industry today. However, Merida Aerospace, a Tampa, Florida-based new space start-up, has been working since its inception in 2019 on its innovative concept known as the Space of Things (SoT). This concept aims to bridge the existing gaps in the space sector by offering comprehensive services and solutions catering to needs related to the space industry under one roof.
By unifying all processes within a single company, Merida Aerospace eliminates the need to collaborate with multiple external suppliers, saving time, money, energy, and resources on new space projects. The vision of the SoT was inspired by the concept of the Internet of Things (IoT). Similar to IoT, it seeks to address all inquiries and requests associated with the aerospace industry. However, unlike IoT, it manifests in the real world, providing a one-stop platform for comprehensive space-related services and products. It can be likened to the Amazon of Space, where anything related to the aerospace industry can be found.
Merida Aerospace offers services through vertical integration, including rocket launch systems, satellites, space data collection, ground control systems for satellites, deep space, rover design and manufacturing, and operating systems for planetary exploration. This comprehensive approach was conceptualized after extensive market research and analysis of private organizations operating in this sector.
Merida Aerospace believes the SoT concept is set to change the space industry, driving growth and acceleration while enabling the creation of projects in a fluid and sustainable manner. It has the potential to expedite aerospace missions funded by private investors and companies, and provide commercial clients with faster access to aerospace products and services. With a team dedicated to addressing client-specific needs from design to manufacturing to project deployment into orbit, Merida Aerospace offers a platform that previously didn’t exist, enabling clients to find everything they need in one place.
This concept establishes a one stop shop for the space industry, allowing clients to complete their individual projects more efficiently and economically.
NEWS

SpaceX Transporter-8 carries 6 satellites into orbit
Six NanoAvionics manufactured satellites went into orbit aboard SpaceX’s Transporter-8 mission.
One of them, Tiger-4, belonging to telecoms operator OQ Technology, will expand the largest 5G Narrowband-IoT constellation in low Earth orbit (LEO). The 6U nanosatellite is the fourth satellite manufactured for OQ Technology by NanoAvionics.
The second one, a 16U optical Earth observation satellite – GEI-SAT – is owned by Satlantis, a Spain-based developer and manufacturer of Earth & Universe Observation payloads for small satellites. The satellite’s a precursor of Satlantis’ remote sensing constellation intended to perform atmospheric CH4 measurements with high spatio-temporal resolution and simultaneous geolocation of source emitters. NanoAvionics supplied the mission with its M16P satellite bus and mission integration services.
The other four satellites include one nanosatellite for remote sensing mission using radio frequencies, two technology demonstration satellites, and an MP42H microsatellite for an orbital reconnaissance demonstration. The latter will take highly accurate measurements of spacecraft and objects in orbit to reduce the threat of collisions.
All satellites were manufactured at NanoAvionics’s manufacturing, assembly, integration, and testing (MAIT) facility in Vilnius, Lithuania, for serial small satellite production for constellations by commercial, civil, and governmental organizations.
NanoAvionics
Explore the September 2023 Issue
Check out more from this issue and find your next story to read.
Latest from Aerospace Manufacturing and Design
- 2024 Favorites: #10 Article – How 3D-printed aviation parts can accelerate return to air
- 2024 Favorites: #10 News – Boom Supersonic completes Overture Superfactory
- OMIC R&D hosts Supporting Women in Manufacturing Day 2024
- 4D Technology's AccuFiz SWIR interferometer
- Seventh Lockheed Martin-built GPS III satellite launches
- KYOCERA AVX's CR Series high-power chip resistor
- UT researchers receive Air Force grant for wind tunnel
- Monticont's linear voice coil servo motor